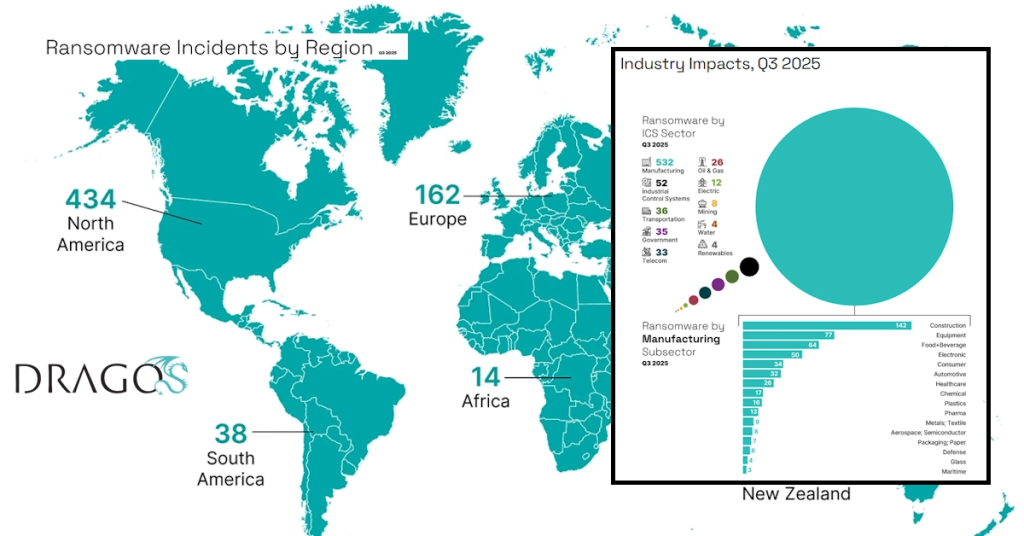
Operational Technology (OT) cybersecurity incidents have surged in recent years, particularly in industrial sectors like mining, metals, and manufacturing. Ransomware remains the dominant threat, often spilling from IT into OT due to poor segmentation, leading to production halts, financial losses, and safety risks. Reports from Dragos (2025 OT Cybersecurity Year in Review), MM-ISAC, and others highlight a tripling of mining cyberattacks from 2023 (10 incidents) to 2024 (30), with ransomware impacting OT in 75-100% of cases in some analyses. Below are key case studies from 2019–2025, focusing on metals/mining where possible.
1. Norsk Hydro Ransomware Attack (2019) – Aluminum Sector Benchmark
- Details: LockerGoga ransomware infected IT systems, spreading to OT and forcing manual operations at extrusion plants and smelters. Affected 35,000+ employees across 40 countries.
- Impact: Production halted/reduced (e.g., 50% in Extruded Solutions); ~$70M recovery costs (no ransom paid).
- Cause: Initial IT breach; lack of segmentation allowed OT spillover.
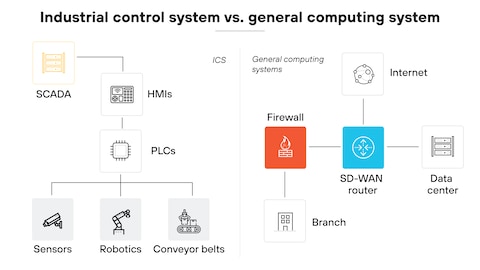
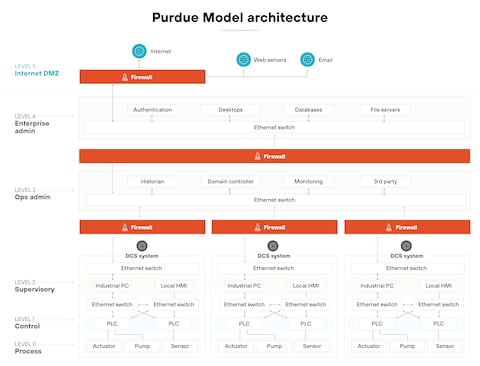
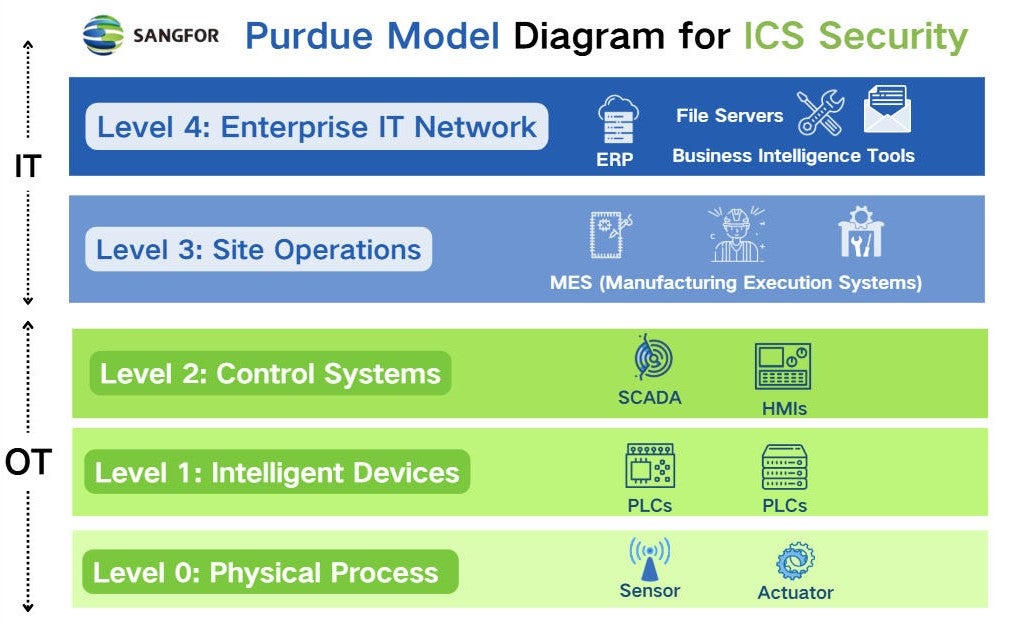
- Lessons: Highlighted IT/OT convergence risks; spurred industry focus on Purdue Model segmentation and zero-trust.
2. Northern Minerals (March 2024) – Rare Earths Mining
- Details: BianLian ransomware group attacked, exfiltrating data.
- Impact: Data breach; operational disruptions undisclosed but typical for mining (e.g., delayed processing).
- Cause: Likely phishing or vulnerability exploitation.
- Lessons: Underscores ransomware targeting critical minerals supply chains.
3. Evolution Mining (August 2024) – Gold Mining
- Details: Ransomware hit IT systems, with potential OT ripple effects in autonomous ops.
- Impact: IT disruptions; production impacts not fully public but aligned with sector trends (partial/full shutdowns).
- Lessons: Australian mining vulnerability amid 40% of METS firms attacked annually.
4. Broader Mining Sector Trends (2024–2025)
- MM-ISAC Data: Attacks tripled (10 in 2023 → 30 in 2024); preliminary 2025 data suggests continued rise.
- Other Incidents: Alamos Gold (2024, BlackBasta); Stillwater Mining (RansomHub data theft). Many involve third-party access (76% of cases).
- Impact: Downtime, revenue loss; e.g., manual shifts in processing/hauling.
5. Dragos-Tracked OT Disruptions (2024–2025)
- FrostyGoop Malware (Jan 2024): Targeted Ukraine energy (district heating outage for 600+ buildings); demonstrates OT-specific wipers.
- General Ransomware: 87% YoY increase in industrial incidents (2024); 75% caused partial OT shutdowns, 25% full.
- Groups: Qilin, CL0P, Lynx active; exploited vulnerabilities (e.g., FortiGate, Cleo file transfer).
Common Themes & Diagrams
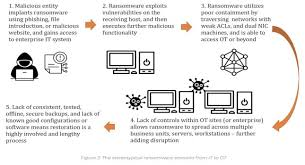
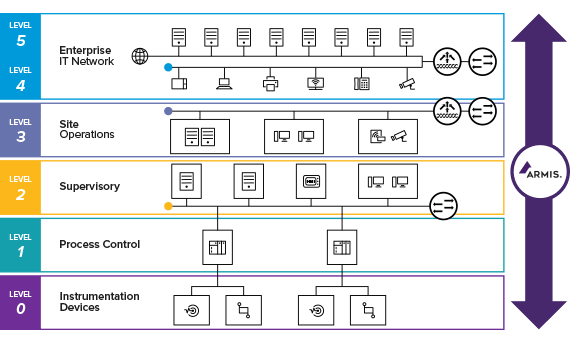
Many breaches exploit flat networks, bypassing Purdue Model segmentation (below: typical breach path via poor IT/OT boundaries).



| Case | Year | Sector | Threat | Impact | Key Lesson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norsk Hydro | 2019 | Aluminum | LockerGoga Ransomware | $70M, manual ops | Segmentation critical |
| Northern Minerals | 2024 | Rare Earths Mining | BianLian Ransomware | Data breach | Supply chain targeting |
| Evolution Mining | 2024 | Gold Mining | Ransomware | IT/OT disruption | Regional hotspots (Australia) |
| Sector-Wide (MM-ISAC) | 2024 | Mining/Metals | Various Ransomware | 3x incidents | Third-party risks (76%) |
These cases emphasize proactive defenses: micro-segmentation, visibility, and zero-trust OT architectures to contain breaches and maintain availability in Mining 4.0 environments.
